Education
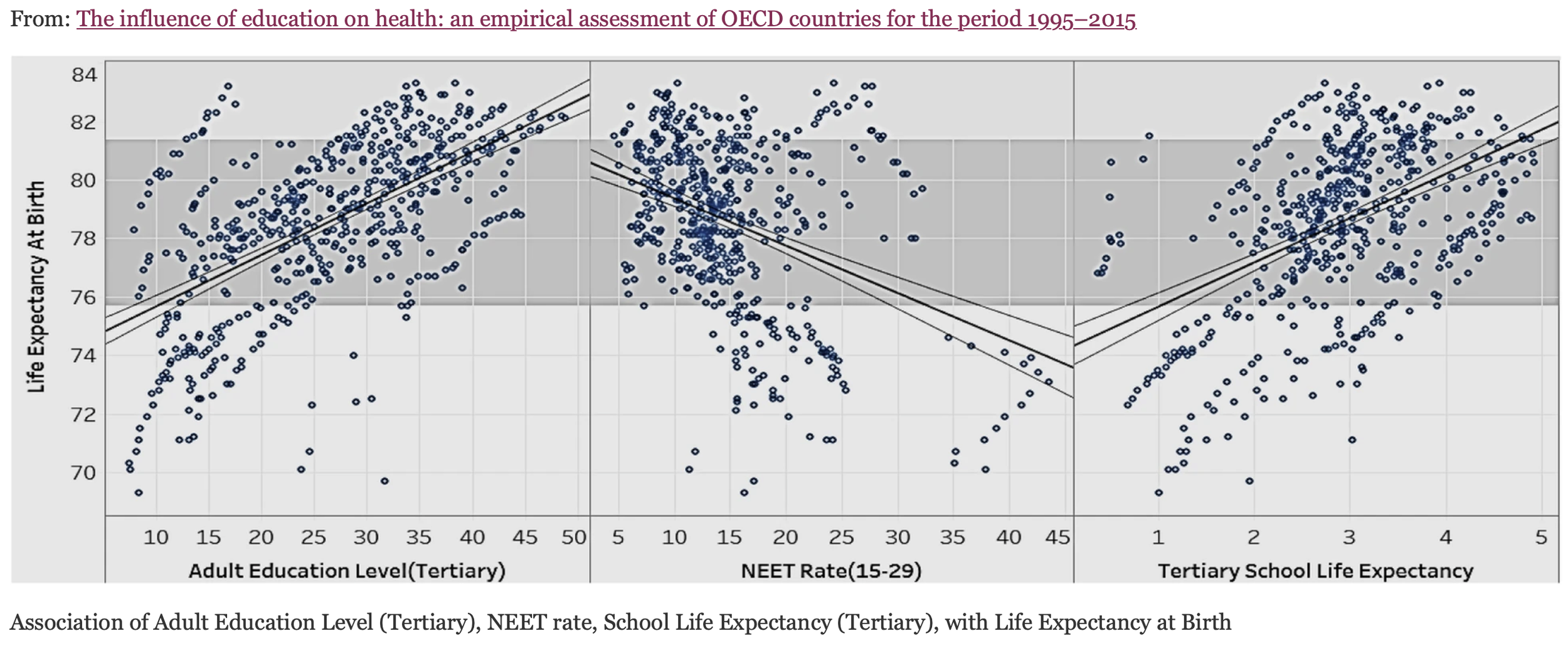
According to the United Nations, there are approximately 262 million children and youth worldwide who are not in school, and more than half of them live in countries affected by conflict or disaster. Individuals with low levels of education are more likely to experience poverty and its associated effects, such as limited access to healthcare, housing insecurity, and food insecurity. The graph to the right shows the relationship between education and life expectancy. Thus, improving access to education is not only a matter of promoting individual well-being, but also of addressing broader societal challenges such as poverty, inequality and mortality.